-
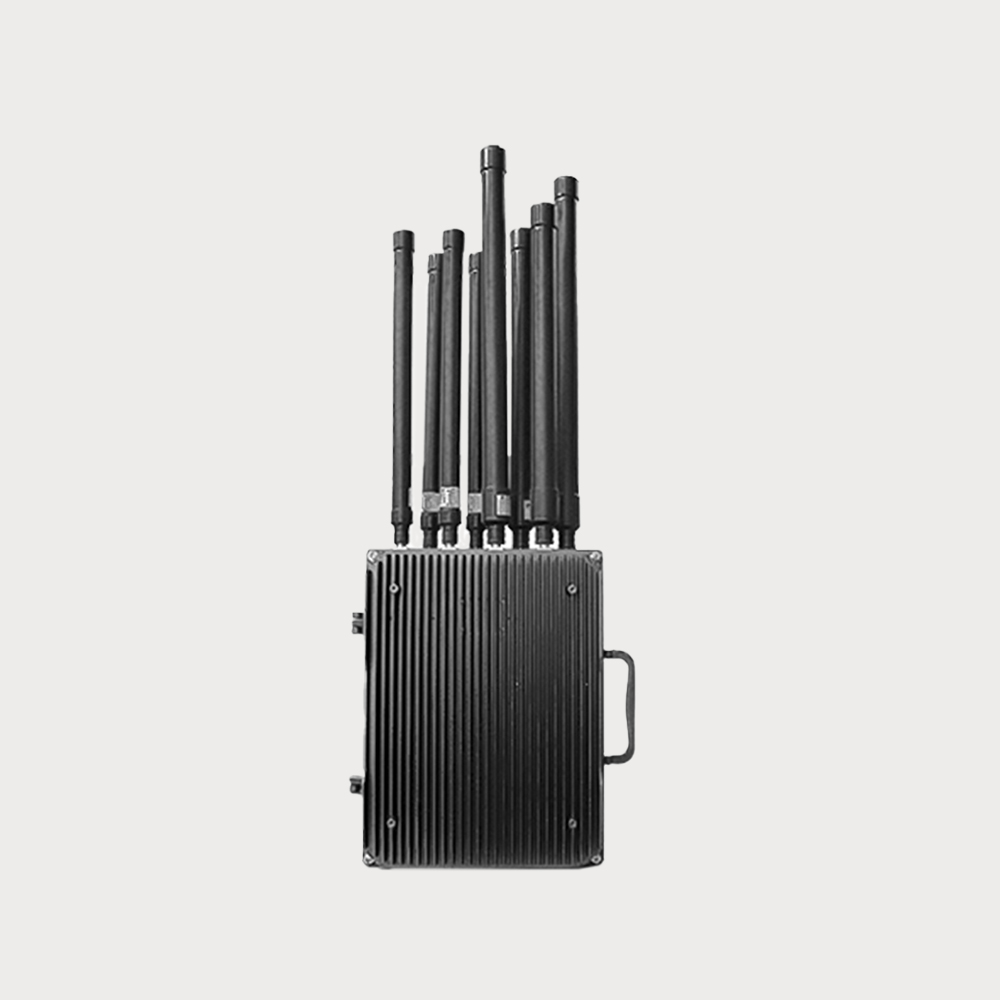
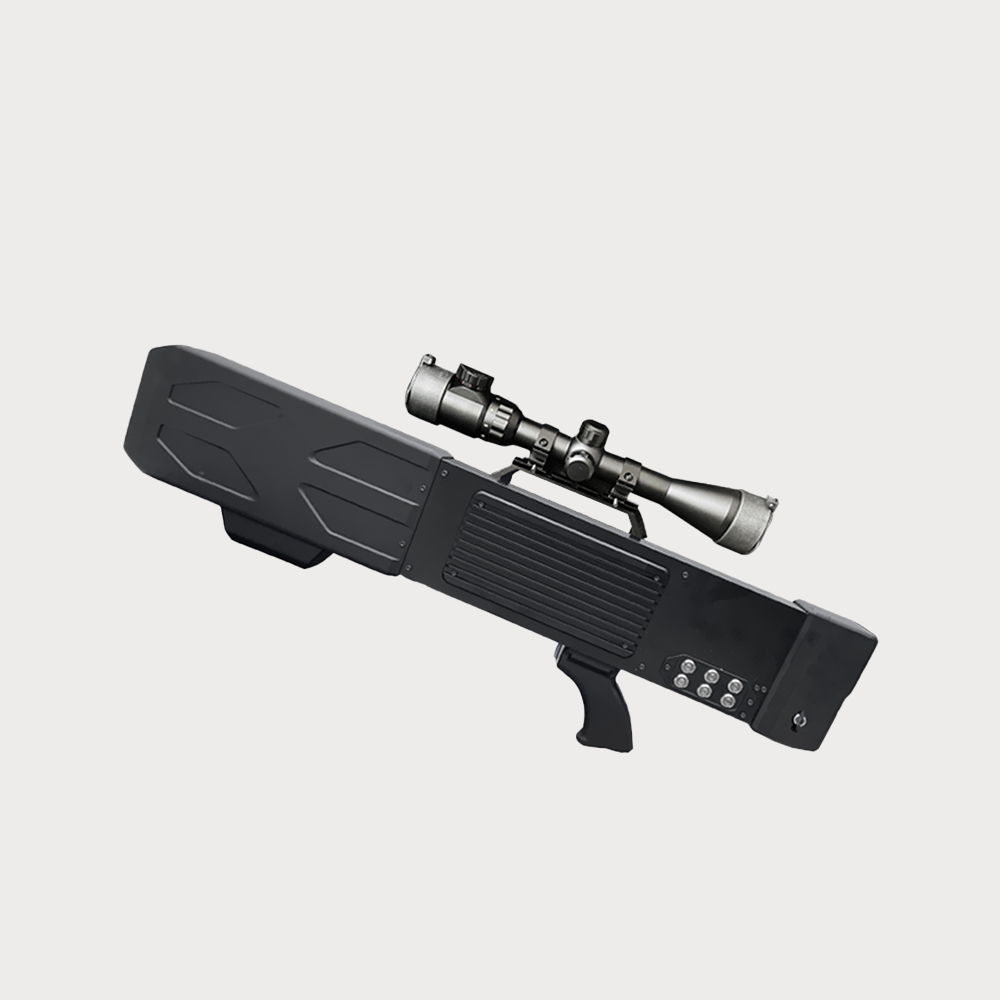
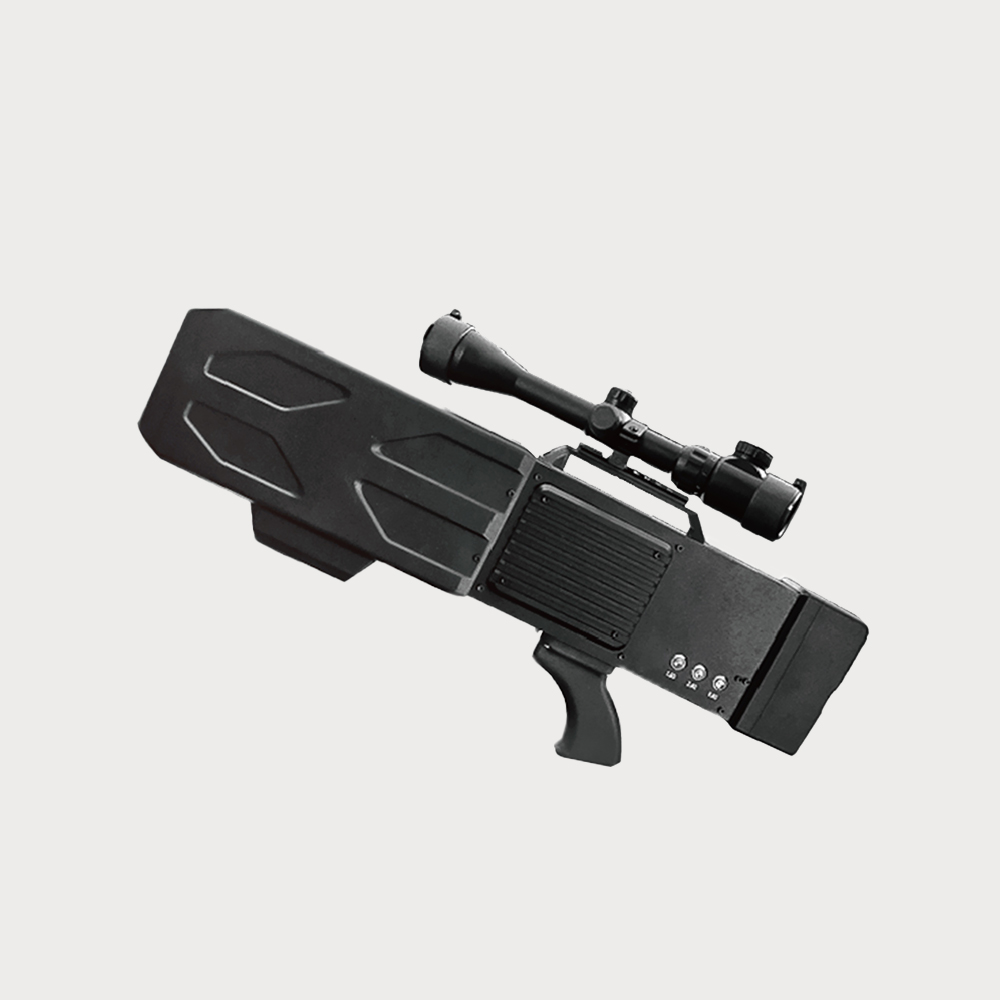
Disabling the drone's satellite navigation, wireless remote control, and wireless video transmission links forces the drone to hover in place, land, or return to the original route. Compared to omnidirectional jamming, the strike is accurate
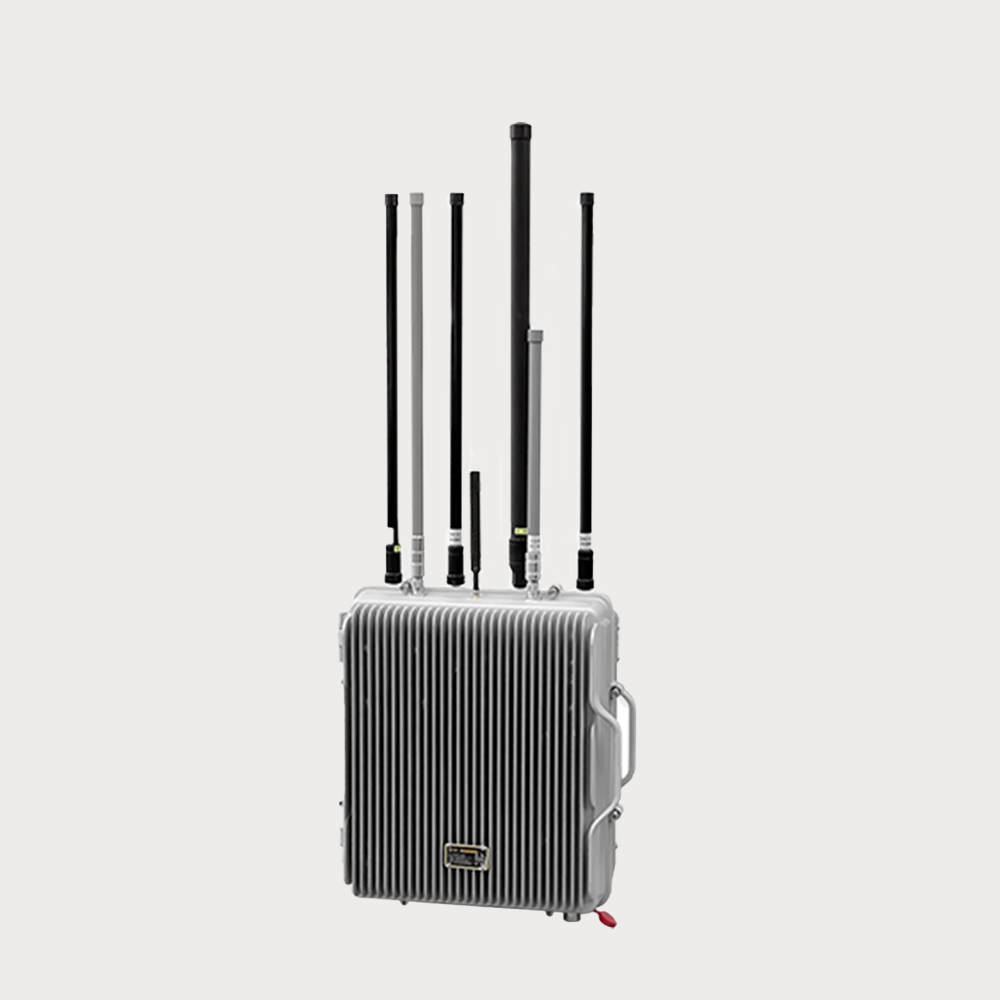
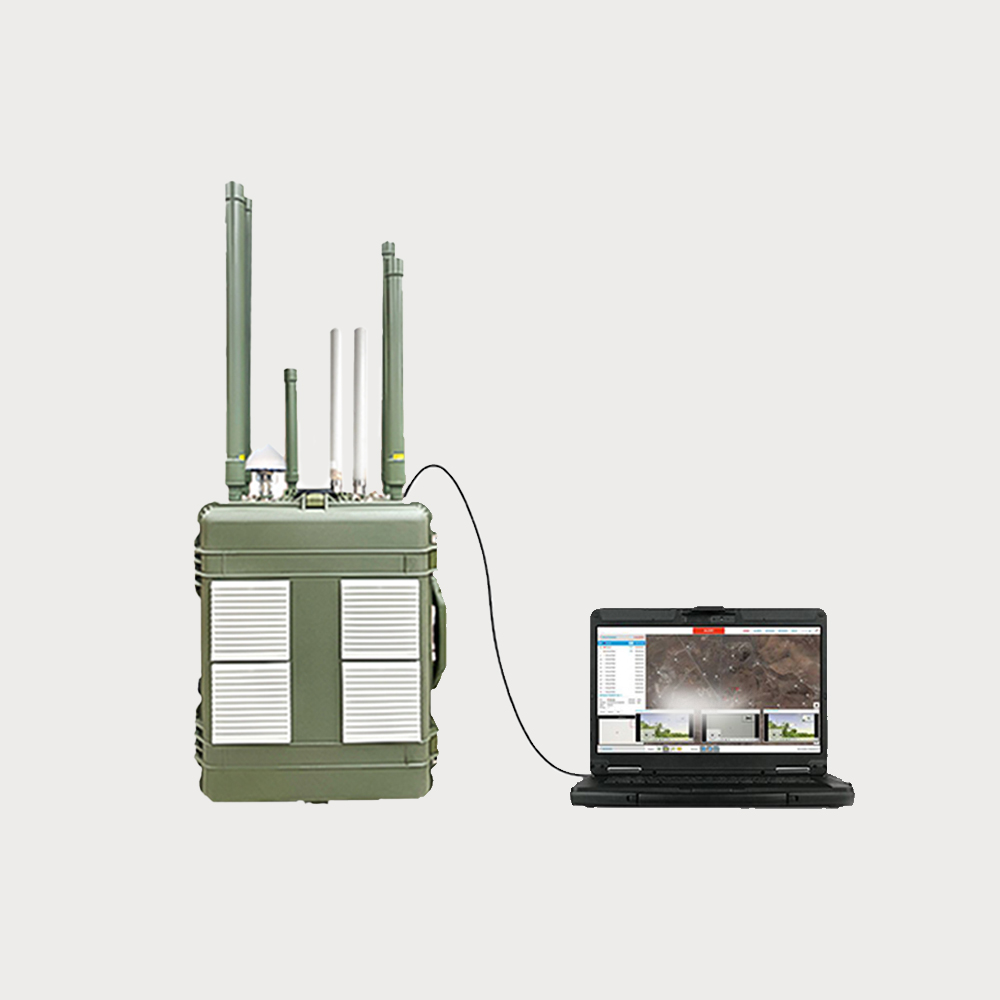
- The device is mainly used for signal interference of UAV, and can be combined with the detection equipment of UAV to form an intelligent linkage defense system.
- $ 97110
- 0 in Stock NowJR-MD1128
-
GROUP
JR1128
-
QUANTITY
- Contact Online
• Expandable integration with radio detection systems, drone detection radar, and other detection systems, achieving integrated drone detection and countermeasure capabilities, supporting both standalone operation and networked operation with multiple devices.
• In open unobstructed areas, the jamming radius can reach up to 1.5 kilometers, and up to 1 kilometer in urban environments.
• The device offers multiple operational modes, forcing drones to return, land, hover, or disrupting their video transmission.
• Can precisely counter and jam commonly used drone frequencies, including 900M, 2.4G, 5.8G, and 1.5G (GPS/GLONASS/Beidou), either simultaneously or independently, with high interference effectiveness.
• Effective against various consumer drones or model aircraft, such as DJI "Phantom" series multi-rotor drones, small fixed-wing drones, paragliders, and small airships, as well as some military micro or small drones or aircraft.
• Operates normally in foggy or light rain conditions, demonstrating strong environmental adaptability.
• Capable of long continuous operation with low maintenance costs.
The radio jammer uses high-gain omnidirectional radio frequency jamming technology, which can emit powerful radio frequency jamming signals to interfere with suspicious targets, so that it can not use satellite navigation, wireless remote control and wireless picture transmission links, forcing the UAV to stay in place, land or return to the original road.
Its working principle emits high-power radio frequency interference signals, paralyzing the satellite navigation, wireless remote control and wireless picture transmission links of the UAV, forcing the UAV to hover, land or return to the original route.

 0
0